Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis Lab Tests
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that can lead to significant health complications, including pulmonary embolism. Understanding the deep vein thrombosis lab test is crucial for early detection and management of this condition. In this article, we will delve into what DVT is, why lab tests are critical, the types of tests available, how they are performed, and what the results mean.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. This condition can manifest with symptoms such as swelling, pain, and redness in the affected limb. However, many individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms. This silent aspect of DVT necessitates reliable testing methods to identify the presence of clots before they lead to more severe complications.
Importance of Lab Tests in Diagnosing DVT
The role of deep vein thrombosis lab tests is essential in the timely diagnosis and management of DVT. Early diagnosis is crucial as it can help prevent the risk of a thrombus traveling to the lungs, resulting in a potentially fatal pulmonary embolism. Here are some of the primary reasons why these tests are vital:
- Timely Detection: Lab tests can assist in the rapid detection of clot formation.
- Risk Assessment: Understanding the risk factors associated with DVT can guide treatment and preventive measures.
- Guiding Treatment Decisions: Results from lab tests can influence the therapeutic approach, including anticoagulation therapy.
- Monitoring Progress: Regular testing can monitor the effectiveness of ongoing treatment for DVT.
Types of Deep Vein Thrombosis Lab Tests
Several lab tests can help diagnose DVT, with each serving a specific purpose in the diagnostic process:
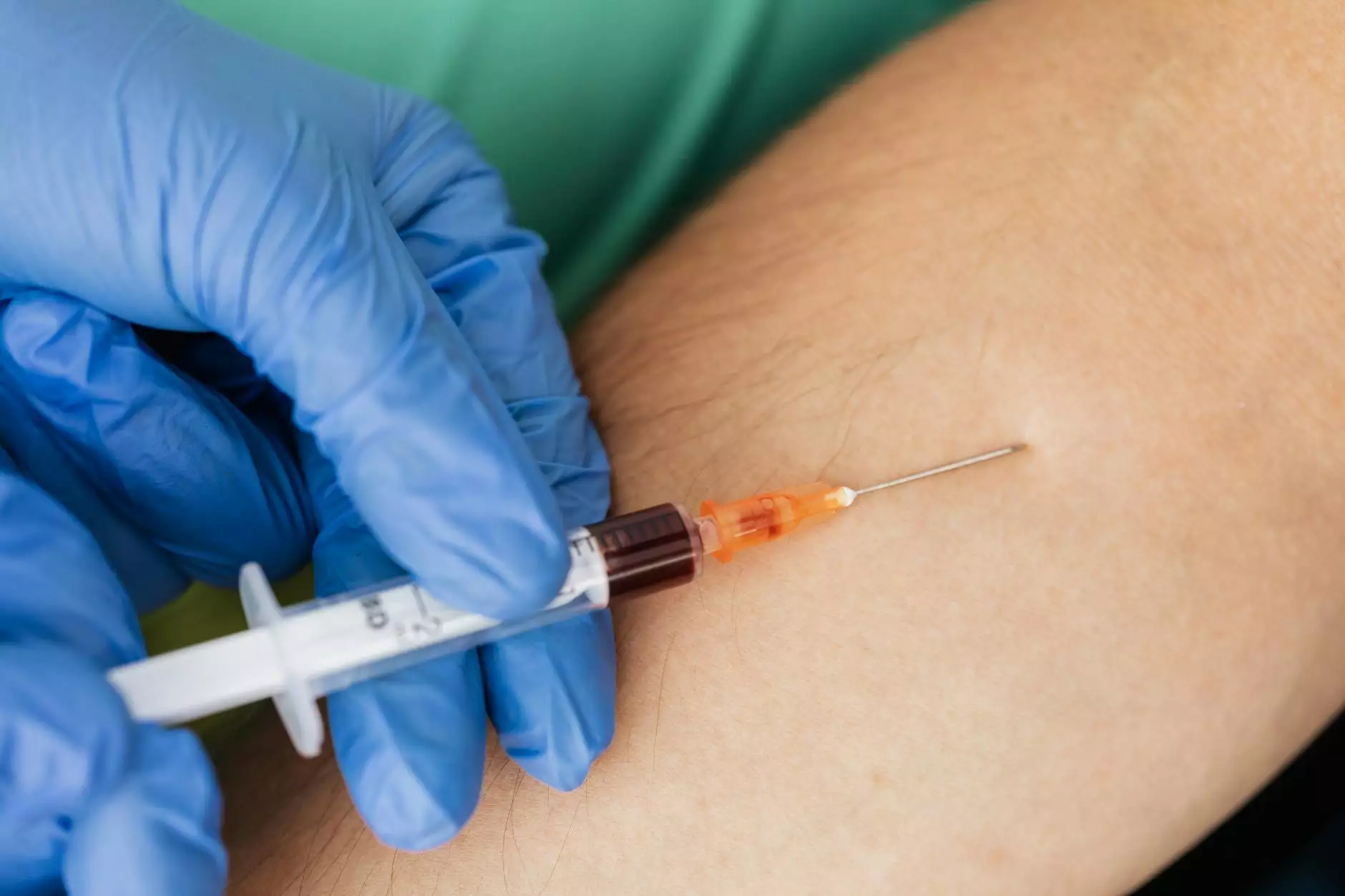
1. D-Dimer Test
The D-dimer test measures the presence of fibrin degradation products in the blood. High levels indicate the possibility of a clot somewhere in the body. While it is not specific to DVT, elevated D-dimer levels can warrant further investigation through imaging studies.
2. Ultrasound
While not a lab test in the traditional sense, Doppler ultrasound is a widely used imaging technique that helps visualize blood flow in veins. It is highly effective in diagnosing DVT by identifying thrombus presence in veins.
3. Venography
Venography is an imaging test that uses a special dye injected into the veins to make them visible on X-ray images. This test is less common due to the availability of non-invasive techniques like ultrasound.
4. MRI and CT Scans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans may be used in certain cases to provide comprehensive images of the veins and detect clots that may not be visible through ultrasound.
Procedure for DVT Lab Testing
The procedure for undergoing lab testing for DVT largely depends on the type of test being performed. Here's a breakdown of the typical procedures:
D-Dimer Test Procedure
- Blood Sample Collection: A healthcare professional will collect a small sample of blood from a vein in your arm.
- Laboratory Analysis: The blood sample is then sent to a lab where it will be analyzed for D-dimer levels.
Ultrasound Procedure
- Preparation: There is no specific preparation required for a Doppler ultrasound.
- Exam Process: You will lie down, and a technician will apply ultrasound gel to the area of examination and use a transducer to obtain images of the veins.
- Duration: The process typically takes 30 minutes to an hour.
Venography Procedure
- Preparation: Inform your doctor of any allergies, especially to contrast dye.
- Administering Dye: A contrast dye is injected into one of your veins, usually in your foot or ankle.
- Imaging: X-ray images are then taken to visualize the veins.
Interpreting DVT Lab Test Results
Once the tests are completed, understanding the results is crucial. Here’s what different findings might indicate:
D-Dimer Test Results
Results of the D-dimer test can be classified as follows:
- Normal Levels: A normal D-dimer level makes DVT less likely.
- Elevated Levels: High levels indicate the presence of a clot; however, conditions other than DVT (like infection, surgery, or trauma) could also raise D-dimer levels.
Ultrasound Results
The results from a Doppler ultrasound can be:
- Positive: Indicates the presence of a clot.
- Negative: Suggests that a clot is not present, though follow-up may be required if symptoms persist.
Venography Results
A venography study can report:
- Clots Detected: Shows a blockage in the vein.
- No Clots Found: Indicates no evidence of DVT.
Prevention and Management of DVT
Preventing DVT is essential, especially for those at higher risk. Here are some effective preventive measures:
- Maintain Mobility: Moving regularly, especially during long periods of travel, can help keep blood flowing.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help reduce the risk of clot formation.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps maintain proper blood circulation.
- Medications: For individuals at high risk, doctors may prescribe anticoagulants to prevent a clot from forming.
Conclusion
Understanding the deep vein thrombosis lab test is fundamental for early detection and effective management of DVT. With appropriate testing and interpretation of results, healthcare providers can develop tailored treatment plans that significantly reduce risks and improve patient outcomes. At Truffles Vein Specialists, our team is dedicated to providing the highest quality of care, ensuring that patients have access to the latest diagnostic tools and a comprehensive range of services for vascular health.